20 years ago, or today, if one hears that a CT scan is ordered, it is believed that the case is complicated. Most of the time it’s true too.
The reason being it cost on the higher side and has a big and complicated machine and hard to understand image is given to you.
This article, let us understand the usefulness of the CT scan, and how this technology has helped us to diagnose in a better way.
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan or computed tomography scan also formerly called CAT scan or computed axial tomography combines a sequence of X-ray images taken from various angles throughout your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of your bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues. CT scan images include more information than traditional X-rays.
Wikipedia says “A CT scan or computed tomography scan (formerly known as computed axial tomography or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology (x-ray) to obtain detailed internal images of the body”
Godfrey Hounsfield of EMI Laboratories in the United Kingdom created the first commercially available CT scanner in 1972. Together with a physicist called Dr. Allan Cormack, In 1979, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine. It was started with only head imaging in 1974 but later on, full-body imaging started around 1976 and by 1980 it was used widely.
How a CT scan is done?
How a CT scan is done depends upon the situation you are in. If in a case of emergencies like an accident or any other kind of trauma, the doctor wants to know about the internal injuries they can do a full CT scan to be on the safer side, and if a doctor has prescribed for diagnosis of any disease than a specific part CT scan can be done that way also.
Pre-Scanning
Depending on which part of your body needs to be scanned, you would be asked to take the clothes off and wear a hospital gown. You also have to remove metal objects like jewellery, belts, glasses, dentures, and piercing.
Now regarding eating, if the doctor has prescribed you a CT scan without contrast, then you can eat, drink and even take your medicines but if he has ordered a CT scan with contrast then you are not to eat but can drink clear fluids 3 to 4 hours prior to the scan. Do you have to drink all the barium (contrast) for the CT scan? The doctor or a trained health professional will provide you with the dose and will monitor you while you take the same.
This contrast is given via mouth when your stomach or esophagus is been scanned. It can be injected via IV in your veins if the test is for the liver, urinary tract, or gallbladder. It can be given by enema by inserting it into your rectum to get a clear scan of your intestines. In case it’s a child who is about to get scanned some time doctor advises giving sedatives for the child to remain still and calm for the image to come clear and not get blurred.
CT scan is not a painful process and with new technology, it takes less time to get the scan get completed. The whole process does not take long and in 30 minutes or so the scan is done.
Actual Procedure
CT scanners look like a giant doughnut flipped on its side. You’re resting on a small, motorized table that’s gliding through a tunnel entrance. Straps and pillows might help you stay in place. The table may include a unique cradle that keeps your head stable throughout a head scan.
As the table transports you inside the scanner, detectors and an X-ray tube circle around you. Each turn generates a series of photographs of tiny sections of your body. There might be buzzing and humming sounds.
A technician can see and hear you in a different room. You’ll be able to communicate with the technician over an intercom. Sometimes technicians may ask you to hold your breath to get a clear picture.
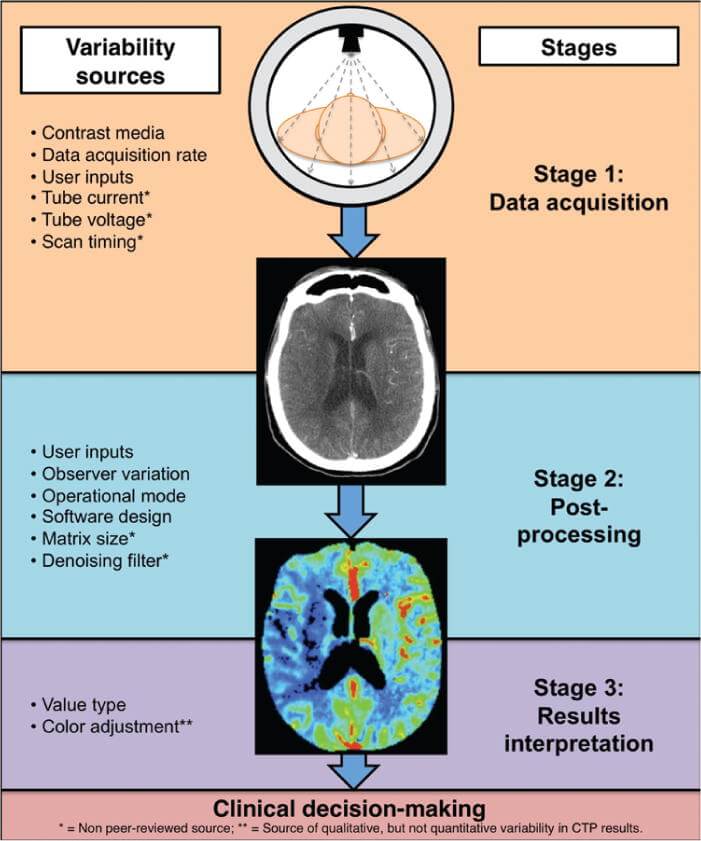
CT machine uses an x-ray generator that rotates around the patient. The X-ray detectors are on the opposite side of the circle from the X-ray source. Depending on tissue density, various tissues attenuate X-rays differently as they travel through the human body. A sinogram is a graphical representation of raw data, however, it is insufficient for comprehension. Following the capture of the scan data, it must be processed using tomographic reconstruction, yielding a sequence of cross-sectional pictures. Small pixel or voxel pieces make up these cross-sectional pictures.

After Procedure
After the exam, you can continue your normal routine. Many times, people have asked why do I feel sick after the CT scan and that can happen if you were given contrast material. In some cases, you may be asked to stay for a short length of time after the exam to ensure that you are feeling well. Following the scan, you will almost certainly be recommended to drink plenty of fluids to help your kidneys remove the contrast material from your body.
Different types of CT
Spiral CT
Rotating tube imaging, commonly known as spiral CT or helical CT, is a technique that requires spinning an entire X-ray tube around the axis of the region being scanned. Because they have been in production for a longer length of time and have a lower cost of manufacture and purchasing, they are the most prevalent types of scanners on the market. The mass and inertia of the equipment (X-ray tube assembly and detector array on the opposite side of the circle) limit the speed at which it can spin. Some systems use two X-ray sources with detector arrays offset by an angle to improve temporal resolution.
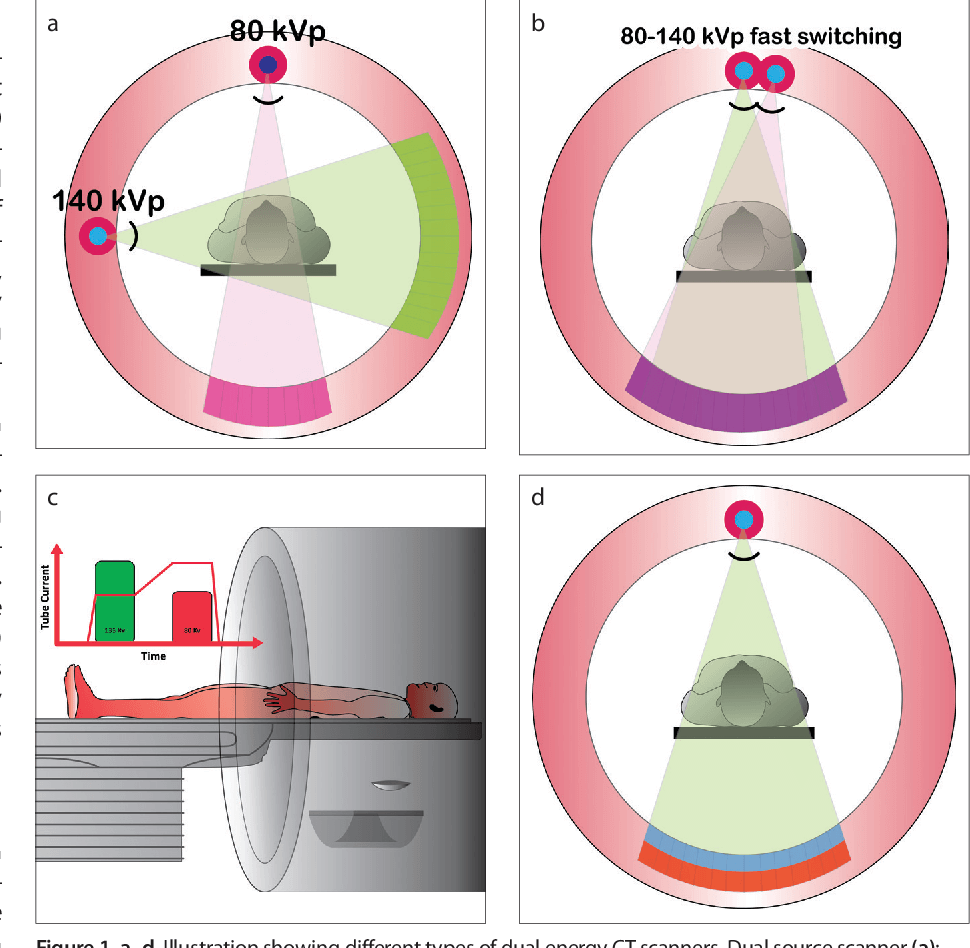
Dual Source CT
Dual-source CT also known as spectral CT is a computed tomography technique that uses two unique x-ray photon energy spectra to probe materials with varying attenuation characteristics at different energies. In contrast to typical single energy CT, which produces a single image set, dual-energy data (attenuation values at two energy spectra) may be used to reconstruct a number of image forms.
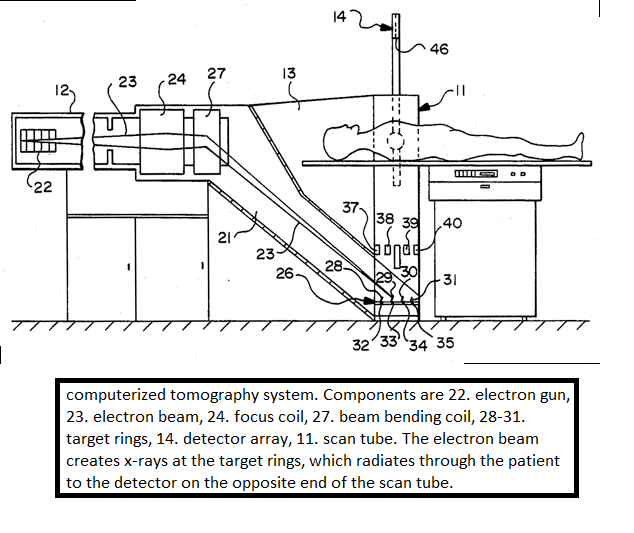
Electron Beam Tomography
The X-ray tube is not manually rotated to rotate the X-ray photon source in EBCT. This one-of-a-kind design was created to more accurately mimic cardiac components that are constantly moving and complete a full cycle of movement with each beating.
Like in typical CT technology, the X-ray source-point travels in a circle in space around the subject to be scanned. In contrast, the X-ray tube in EBT is huge and immobile, and it partially encircles the imaging circle. Instead of rotating the tube, the electron-beam focus point (and hence the X-ray source point) is electronically swept along the tube’s tungsten anode, tracing a vast circular arc on its inner surface.
The fundamental application benefit of EBT machines, and the justification for their development, is that the X-ray source-point may be swept at a significantly quicker pace since it is swept electronically rather than manually.
CT perfusion imaging
CT perfusion imaging is a type of CT that measures blood artery flow while administering a contrast agent. Blood flow, transit time, and organ blood volume may all be calculated with great accuracy and precision. Although this form of CT may be used on the heart, its sensitivity and specificity for detecting abnormalities are still lower than other types of CT. This approach can also be used on the brain, because CT perfusion imaging may identify poor brain perfusion considerably earlier than a regular spiral CT scan. In terms of stroke diagnosis, this type of CT scan outperforms all others.
What is a CT scan used for?
Since its introduction in the 1970s, computed tomography (CT) has been a valuable tool in medical imaging, augmenting X-rays and medical ultrasonography. Recently, it has been used in preventive medicine or disease screening, such as CT colonography for individuals at high risk of colon cancer or full-motion heart scans for those at high risk of heart disease. Various institutions provide full-body scans to the general public, despite the fact that doing so defies the advice and official stance of several professional organizations in the field, owing mostly to the radiation dose employed.
CT scan is used for scanning the following
Head CT scan
CT scans of the head are widely used to detect infarction (stroke), malignancies, calcifications, haemorrhages, and bone fractures. Hypodense (dark) structures can indicate edoema and infarction, calcifications and haemorrhages, and bone fractures can be seen as disjunction in bone windows. Tumours are identified by the swelling and anatomical distortion, as well as by the edoema that surrounds them. The N-localizer device is used in CT-guided stereotactic surgery and radiosurgery to treat brain tumours, arteriovenous malformations, and other surgically treatable illnesses
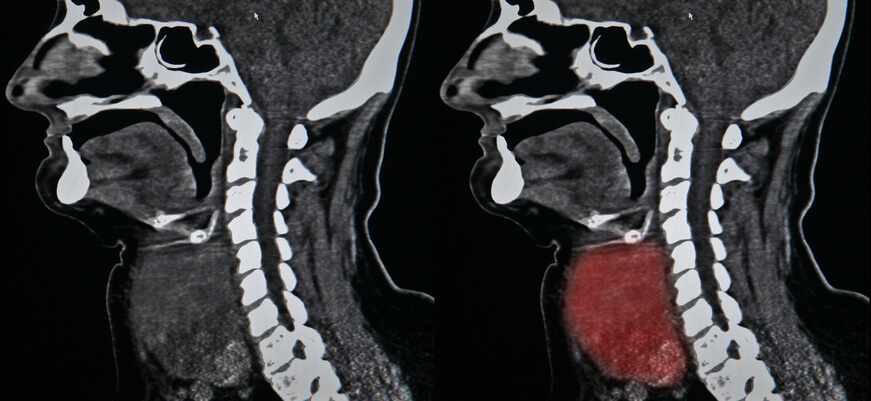
Neck CT scan
In most cases, contrast CT is the initial study of choice for individuals with neck masses. Thyroid computed tomography (CT) is useful in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Because CT scans frequently uncover thyroid abnormalities by chance, they are frequently the favored investigative technique for thyroid abnormalities.
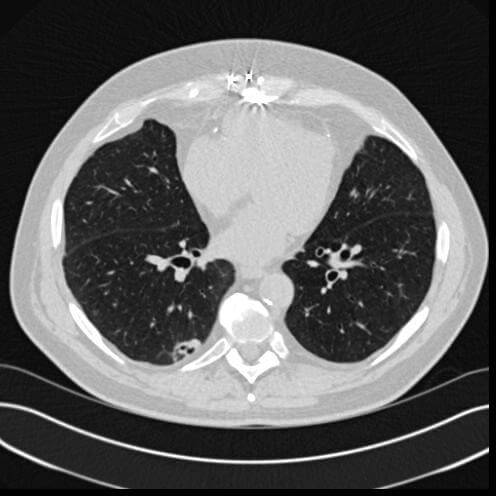
Lung CT scan
A CT scan can detect both acute and chronic abnormalities in the lung parenchyma, or the tissue of the lungs. It is especially crucial in this scenario because normal two-dimensional X-rays do not detect such problems. Various procedures are used depending on the suspected condition. Thin sections with high spatial frequency reconstructions are used to examine chronic interstitial processes like emphysema and fibrosis; scans are often performed on both inspiration and expiration. This specialist technique, known as high-resolution CT, produces a sampling of the lung rather than continuous images.
Angiography
Computed tomography angiography (CT angiography or CTA) is a computed tomography technique used for angiography (the examination of arteries and veins) throughout the human body. Images are created by injecting contrast dye into the blood vessels to look for blockages, aneurysms (wall dilatation), dissections (wall tearing), and stenosis (narrowing of a vessel). CTA can visualize the vessels of the heart, the aorta, and other large blood arteries, the lungs, the kidneys, the head and neck, and the arms and legs.
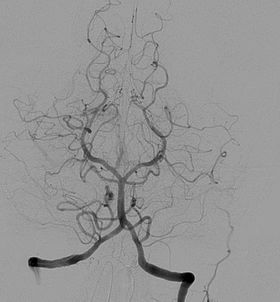
Heart (Cardiac) CT scan
A heart CT scan is used to learn about cardiac or coronary anatomy. Traditionally, cardiovascular CT scans have been used to discover, diagnose, or monitor coronary artery disease. CT has recently played a key role in the rapidly expanding field of transcatheter structural cardiac surgeries, notably in the transcatheter repair and replacement of heart valves.
The main two forms of Cardiac (Heart) CT scan are coronary CT angiography to evaluate the coronary arteries of the heart and coronary CT calcium scan is used to check the severity of the coronary artery disease.
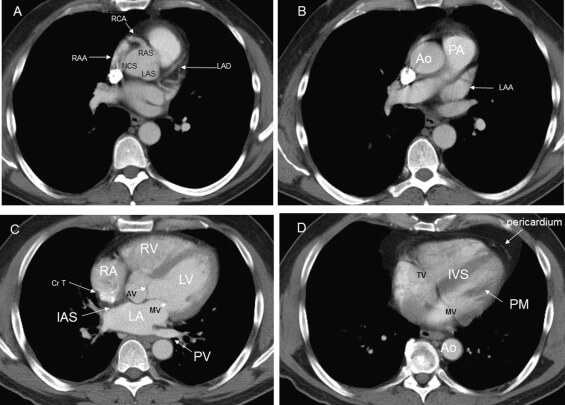
Abdomen and Pelvis CT scan
Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis is a sensitive method for identifying abdominal diseases (CT). It is widely used to determine the stage of cancer and to monitor its development. It can also be utilized to investigate acute stomach discomfort (especially in the lower quadrants, for right upper quadrant pain, ultrasound is the preferred first-line investigation). Renal stones, appendicitis, pancreatitis, diverticulitis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, and intestinal obstruction are all easily spotted and examined with CT. CT is also the first line of defense for detecting solid organ damage after trauma.
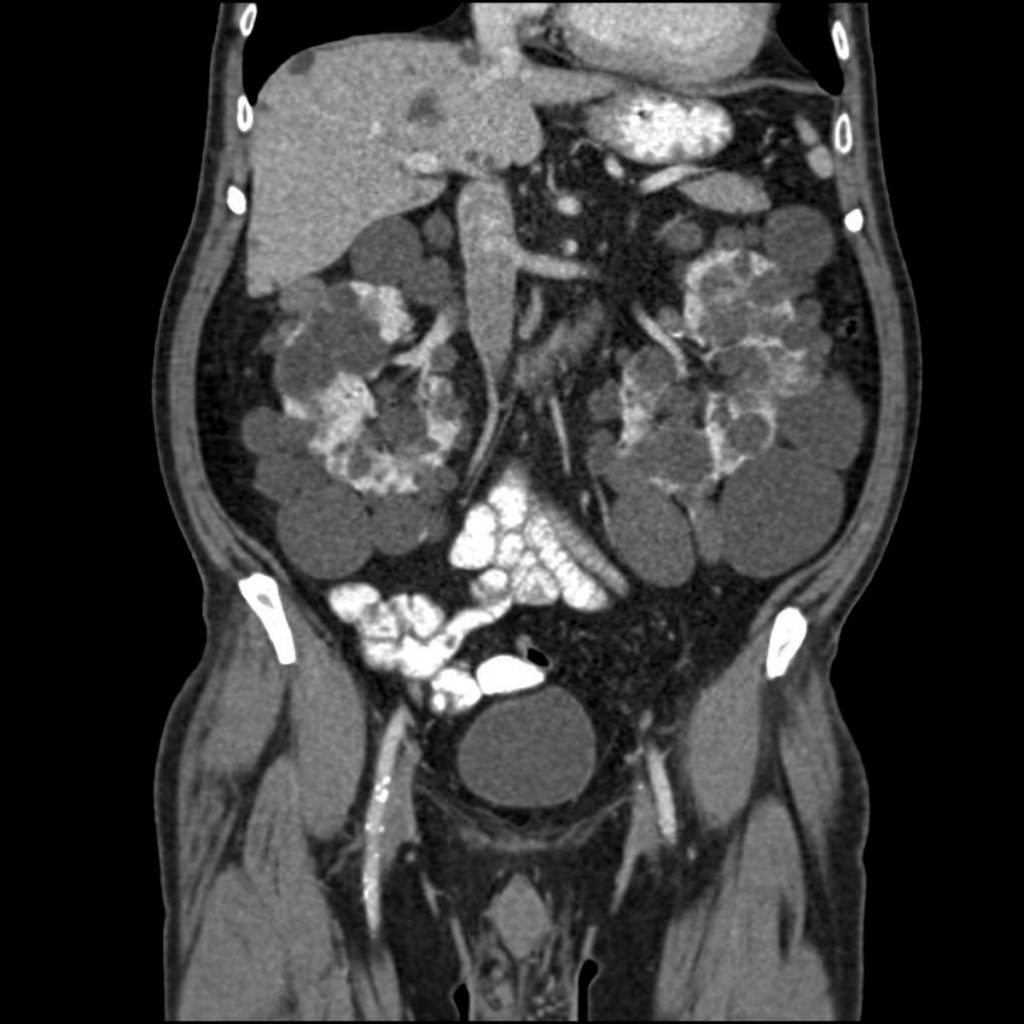
Axial skeleton & Extremities (Fractures) CT scan
CT is widely used to scan complex fractures in the axial skeleton and extremities because of its ability to reproduce the region of interest in several planes. Fractures, ligamentous injuries, and dislocations can be easily detected with a 0.2 mm resolution. There are new uses for sophisticated dual-energy CT scanners, such as aiding in the diagnosis of gout.
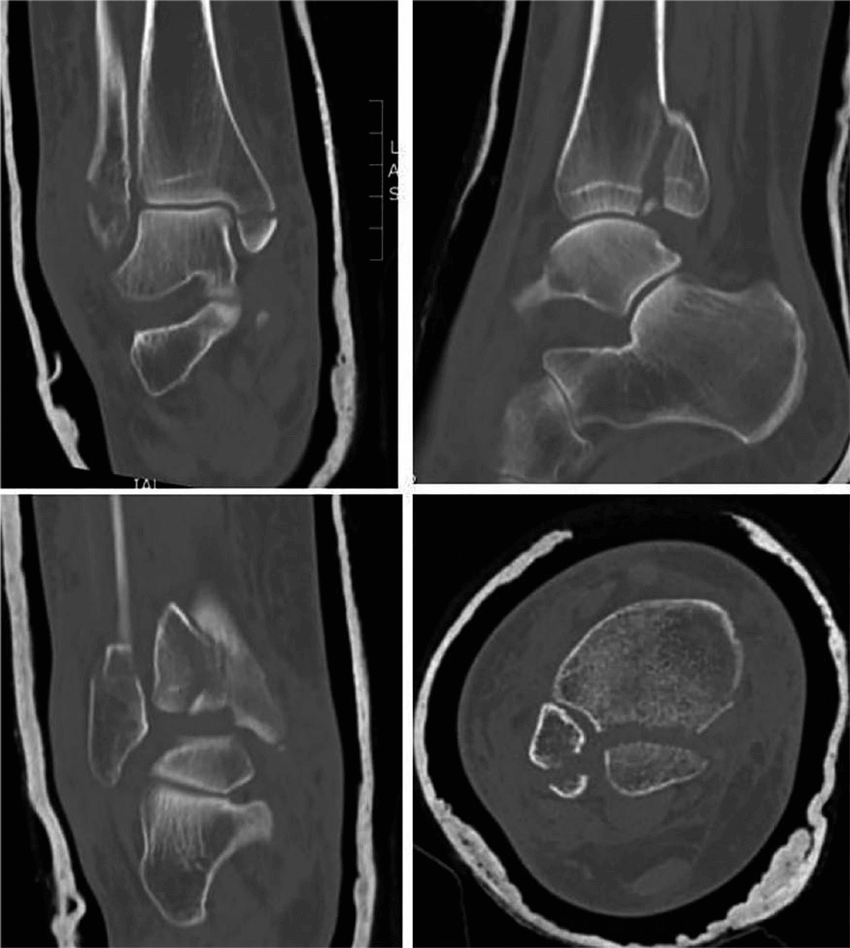
How to read a CT scan
It is critical to know the direction of a CT scan while interpreting it. Images are most typically displayed in the transverse plane, with the viewer gazing up at the body from the patient’s toes.
The abbreviation RALP might help you gain your bearings. Starting at 9 a.m. and going clockwise in 90-degree increments, we examine the patient’s Right, Anterior, Left, and Posterior aspects.
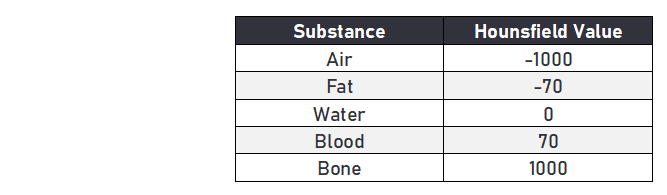
The density of body tissue determines the degree to which x-rays are attenuated.
Tissues with a high attenuation coefficient (strong absorption) look white, while tissues with a low attenuation coefficient (weak absorption) appear black. Radiodensity is measured using the Hounsfield Scale. Tissues with a high Hounsfield score have a high attenuation coefficient, giving them a white appearance.
What is the side effect of CT scan?
Exposure to Radiation
During a CT scan, you are momentarily exposed to ionizing radiation. Because a CT scan obtains more detailed information, the radiation dosage is larger than with a normal X-ray. Low amounts of radiation used in CT scans have not been shown to cause long-term harm, however much higher doses may cause a little increase in your cancer risk.
CT scans provide significant advantages that far outweigh any potential hazards. Doctors use the least amount of radiation possible to acquire the required medical information. Furthermore, newer, faster technology and processes use less radiation than formerly used. Discuss the advantages and dangers of your CT scan with your doctor.
Harmful to unborn babies
If you are pregnant, notify your doctor. Although the radiation from a CT scan is unlikely to damage your baby, your doctor may recommend another type of screening, such as an ultrasound or an MRI, to prevent exposing your baby to radiation. The low doses of radiation utilized in CT imaging have had no negative effects on humans.
Many people do ask before taking a CT scan, what is the best CT scan or MRI. To answer that MRIs and CT scans may both be used to visualize inside body structures. A CT scan, on the other hand, is less time-consuming and may provide pictures of tissues, organs, and skeletal structures. An MRI is incredibly capable of producing images that help doctors determine whether or not there are abnormal tissues within the body. MRIs provide more detailed images.
Adverse reaction to the contrast material
In some cases, your doctor may recommend that you obtain a specialized dye called a contrast material. This might be something you consume before your CT scan or something injected into your rectum via a vein in your arm. Although it is rare, the contrast chemical can cause medical problems or allergic reactions.
The vast majority of reactions are mild, resulting in a rash or itching. In rare situations, an allergic reaction might be severe, even deadly. If you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast material, tell your doctor.
Conclusion
Looking ahead, the future of CT is expected to be automated and faster, and easier to scan. With AI in the mix, the technology with the new model itself CT scanner from a tool of interpretation to a machine providing speedier and more direct with detail diagnosis.
The global demand for CT scanners is going to rise to a CGAR of 5.9% from 2019 to 2022 to a value of 6429.8 million. The new scanners with 320 detectors rows are coming into the market which provides an image of the larger part of the body at a single time along with powerful x-dray beams.
In general, whenever a doctor advised a CT scan you should go for the same and get it done so that the diagnosis can be made basis the result and treatment can be started rather than be fearful of radiation.
what is contrast in CT scan
Barium is given as a contrast to the patient for a clear image. This can be given via oral, IV or PR (rectal) depending upon the area of scan.
Does DNA repair itself after CT scan?
Yes after the scan DNA does get repaired in time. The damage itself is very minimal to start with.
Are CT scans safer now?
According to research, the risk of cancer from CT scans is quite low. Your medical condition may necessitate an ionizing radiation imaging scan at times. If you have any reservations, speak with your doctor about the necessity for and significance of the exam.


1 thought on “CT scan 101: The Essential Guide”
Pingback: What is a diagnostic center : The Essential Guide